Configuration Bench
Fentrica's Bench is a powerful, flow-based development tool designed for wiring together hardware devices, APIs, and online services. It provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to wire together flows using a wide range of nodes in the palette, all of which can be deployed to the runtime in a single click.
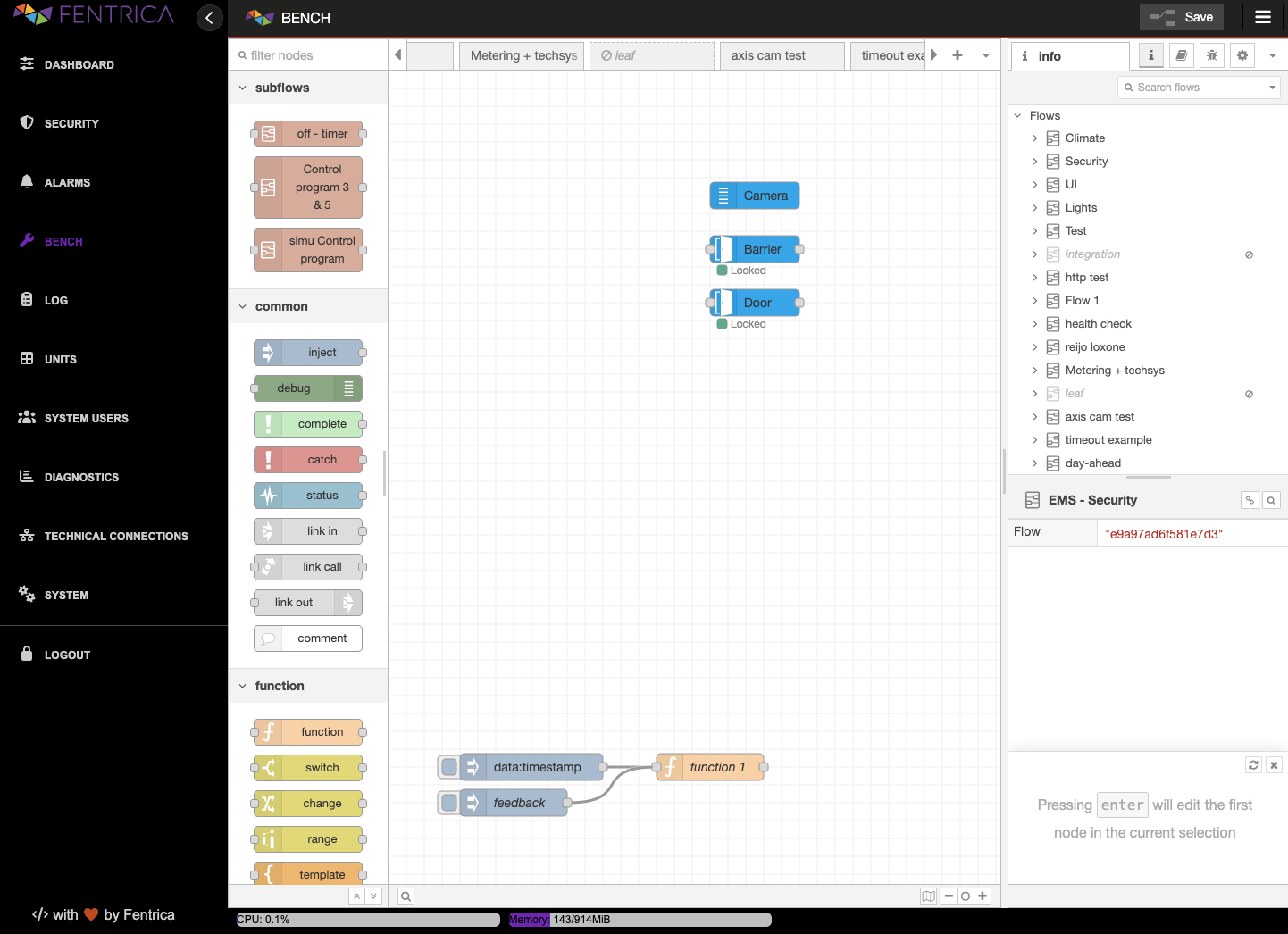
Core Features
Visual Flow-Based Programming
Fentrica's Bench utilizes a flow-based programming model that represents applications as a network of "black box" processes, which exchange data across predefined connections. These black boxes are known as nodes.
- Visual Editor: A drag-and-drop interface running in your browser.
- Rapid Development: Quickly prototype and build applications by connecting pre-built blocks.
- Event-Driven: Ideal for handling event-driven applications, data acquisition, and processing.
Lightweight Runtime
The runtime is architected to be highly efficient and lightweight, taking full advantage of an event-driven, non-blocking model. This allows Fentrica's Bench to run effectively on low-cost hardware at the edge of the network as well as in the cloud.
Portable Configuration
Flows created in Fentrica's Bench are stored as standard JSON configurations. This makes it incredibly easy to import, export, and share your logic and configurations with others or version control systems.
Key Concepts
Nodes
Nodes are the fundamental building blocks of Fentrica's Bench.
- Input Nodes: Generate data (e.g., inject a timestamp, receive an HTTP request, listen for MQTT messages).
- Processing Nodes: Transform, filter, or route data (e.g., run JavaScript functions, switch based on conditions, parse JSON).
- Output Nodes: Send data to external systems (e.g., make an HTTP request, publish to MQTT, write to a file, view in the debug panel).
Wires
Wires connect the output ports of one node to the input ports of another. They represent the path that messages travel through your application. You can branch wires to send a message to multiple downstream nodes simultaneously.
Messages (msg)
Data is passed between connected nodes in the form of a JavaScript Object, conventionally referred to as the msg object.
msg.payload: The primary body of the message. This is where most nodes look for data by default.msg.topic: often used to categorize the message.- Custom Properties: You can add any arbitrary property to the
msgobject to carry metadata through your flow.
The Palette
The left-hand side of the editor is the Palette, which lists all available nodes installed in your environment. Nodes are categorized (e.g., Common, Function, Network, Sequence) to help you find what you need.
Working with Fentrica's Bench
1. Creating a Flow
Simply drag nodes from the Palette onto the central Workspace. Connect them by clicking and dragging from the output port of one node to the input port of another.
2. Configuring Nodes
Double-click any node in the workspace to open its Edit Dialog. Here you can configure specific properties for that node, such as API endpoints, function logic, or debug settings.
3. Deploying
Once your flow is constructed, click the Deploy button in the header. This sends your active flow configuration to the server, making it live immediately.
4. Debugging
Use the Debug node to inspect messages passing through your flow. The Debug Sidebar (on the right) displays the contents of messages captured by Debug nodes, allowing you to trace data and identify issues.
5. Built-in Documentation
Every node comes with its own documentation. To view it, simply select a node in the palette or workspace, and the Info tab in the sidebar will display a help file explaining what the node does, its expected inputs, and its outputs. This allows you to learn about new capabilities without leaving the editor.
Advanced Logic (The Function Node)
For logic that goes beyond standard nodes, Fentrica's Bench includes a Function node. This allows you to write custom JavaScript code to manipulate the msg object directly.
Example Function:
// Simple transformation
msg.payload = msg.payload * 2;
return msg;
You can also use multiple outputs in a Function node to route messages to different paths based on logic conditions.
Context (State Management)
While messages pass data between nodes, sometimes you need to store data across different messages or different flows. Fentrica's Bench provides a Context store:
- Node Context: Visible only to the specific node.
- Flow Context: Visible to all nodes on the same flow tab.
- Global Context: Visible to all nodes in the entire editor.
Smart Spaces
Fentrica's Bench is the engine used to build Smart Spaces. By using specific UI nodes, you can quickly build user interfaces with cameras, door controls, and security controls that interact directly with your backend flows. These interfaces allow users to visualize data and control their environments.
For more information on configuring these interfaces, please refer to the Smart Spaces documentation.